Structured Cabling Mistakes That Quietly Kill Network Speed (But Nobody Checks)

You pay for a lightning-fast 1,000 Mbps internet plan. You even upgraded your router. So why does your Netflix still buffer at the worst moment, and why do your Zoom calls freeze when it’s your turn to speak? After resetting everything for the tenth time, it’s natural to blame your internet provider, but often the real problem is hiding in plain sight. The issue isn’t always “out there” on the internet; it’s the forgotten physical wiring snaking through your walls and coiled behind your desk. This is a common but unchecked reason for a slow connection. We spend all our time troubleshooting the wireless devices we see, completely ignoring the physical foundation that makes them work. It's a classic network infrastructure bottleneck that almost no one thinks to investigate. In practice, the quality of your wired network—how the cables are run, where they are placed, and what they’re plugged into—is just as critical as your internet plan. Think of it like a plumbing system: it doesn’t matter how much water pressure the city provides if you have a kink in the hose. A single bad connection or a poorly placed cable can quietly throttle your gigabit highway down to a single-lane dirt road, leaving you wondering, “Why is my wired network so slow?” This guide helps you play detective by uncovering the five most common cabling mistakes that silently kill network speed. You’ll learn how to spot them in your own home or office, giving you a clear path for troubleshooting a slow ethernet connection and finally getting the speed you pay for.
Mistake #1: Using an Outdated Cable from Your Junk Drawer
We all have that one drawer: a tangled mess of old chargers and mystery cords. When you needed to connect your new Smart TV or gaming console, you probably grabbed the first Ethernet cable that fit. This simple act of convenience, however, could be the very reason your connection feels sluggish. Not all network cables are created equal, and using an outdated one is like putting budget tires on a sports car—you'll never reach its top speed, no matter how powerful the engine is. Go take a look at the cable you're using right now. Printed in tiny letters along its rubbery jacket is a "Category" rating. If it says CAT5, you've found your speed thief. Cat5 cables were designed for older, slower networks and physically cannot handle speeds over 100 Megabits per second (Mbps). This creates a permanent bottleneck; even if you pay for a lightning-fast 1,000 Mbps plan, a CAT5 cable will slam the brakes on your entire network. Modern connections require at least CAT5e but ideally CAT6 to deliver the gigabit speeds you expect. The good news is that this is the cheapest, fastest network upgrade you can possibly make. A new CAT6 cable often costs less than a fancy cup of coffee and can instantly unlock the full speed you’re already paying for. Before you spend an hour on the phone with your internet provider, check the text on your cable. However, simply owning the right cable isn't the whole story; what it runs next to can be just as damaging to your speed.
Mistake #2: Running Your Network and Power Cords as Best Friends
Take a quick peek behind your desk or entertainment center. Do you see a neatly bundled collection of cables, with the blue or gray network line zip-tied tightly to the black power cords? While this might look tidy, you’ve accidentally created a major source of slow ethernet connection issues. This problem is called electrical interference, or "crosstalk," and it’s one of the most common reasons for an unstable wired connection. Think of it like trying to have a quiet conversation right next to a shouting rock concert; the power cord’s loud electrical signal completely overwhelms the delicate data signal in the network cable. When this happens, the data flowing through your network cable gets scrambled and corrupted. Your computer or gaming console receives a jumbled mess instead of a clean piece of information—like a garbled sentence from a bad phone call. It then has to stop and ask the router to send that same piece of data all over again. This constant cycle of errors and re-sends creates invisible lag, causing everything from video buffering and choppy Zoom calls to frustrating delays in online games, even when your speed test looks fine. Fortunately, fixing network cable interference is completely free and takes about 30 seconds. Simply unplug the cables, separate them, and run them so there are at least a few inches of open air between your Ethernet lines and any power cords—especially the thick ones going to your computer, monitor, or power strips. Don’t bundle or braid them together. This small gap is often all that’s needed to quiet the "noise" and create a much more stable connection. Just as what a cable runs next to matters, so does its physical shape. Forcing a cable into a sharp turn can be just as damaging.
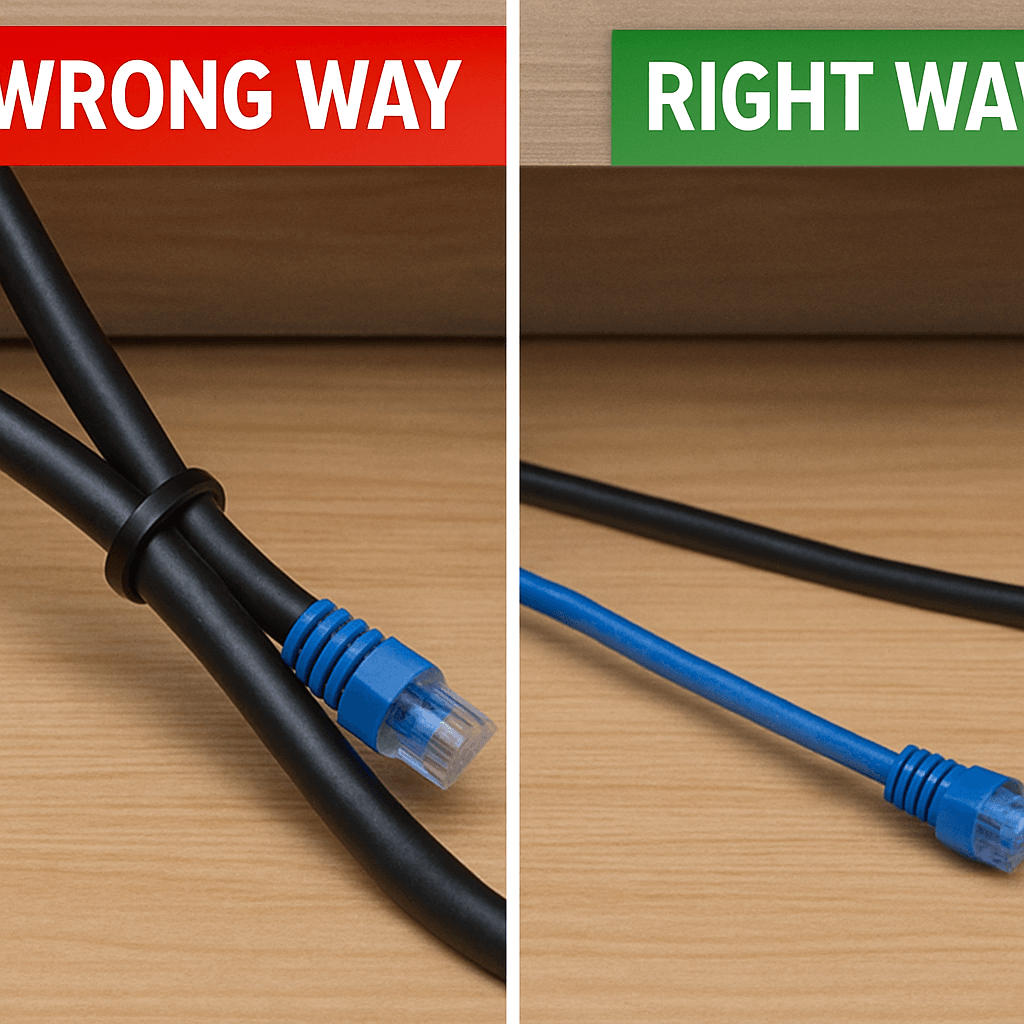
Mistake #3: The Sharp 90-Degree Bend That Kinks Your Data Flow
Just as a cable’s neighbors matter, so does its physical journey. We’ve all done it: bent a cable sharply around a door frame or stapled it tightly to a baseboard to keep things looking clean. While it might be aesthetically pleasing, you’ve just created a physical bottleneck for your data. The best way to understand the impact of an ethernet cable's bend radius is to picture a garden hose. If you put a hard kink in the hose, the water flow slows to a trickle. An Ethernet cable works the same way; a sharp bend damages the delicate, precisely twisted pairs of copper wires inside, restricting the flow of data. This physical damage isn't just a temporary slowdown—it can permanently cripple your connection. When the internal wiring is compromised, data packets can get corrupted or lost entirely. Like a garbled phone call, your computer has to ask for the information to be sent again, creating the same kind of invisible lag and re-sends we saw with electrical interference. To test your network cable quality visually, never bend a cable tighter than the curve of a coffee mug. Always opt for a gentle, sweeping turn. This concept is officially known as "bend radius," and respecting it is crucial for a healthy network. Go check the cables running to your router, smart TV, or home office computer. Do you see any hard creases, tight staples, or sharp 90-degree angles? If you do, gently straightening them into a smoother curve could instantly improve your connection's stability. Just as a cable’s shape matters, so does its total length, which can introduce a whole different set of problems.
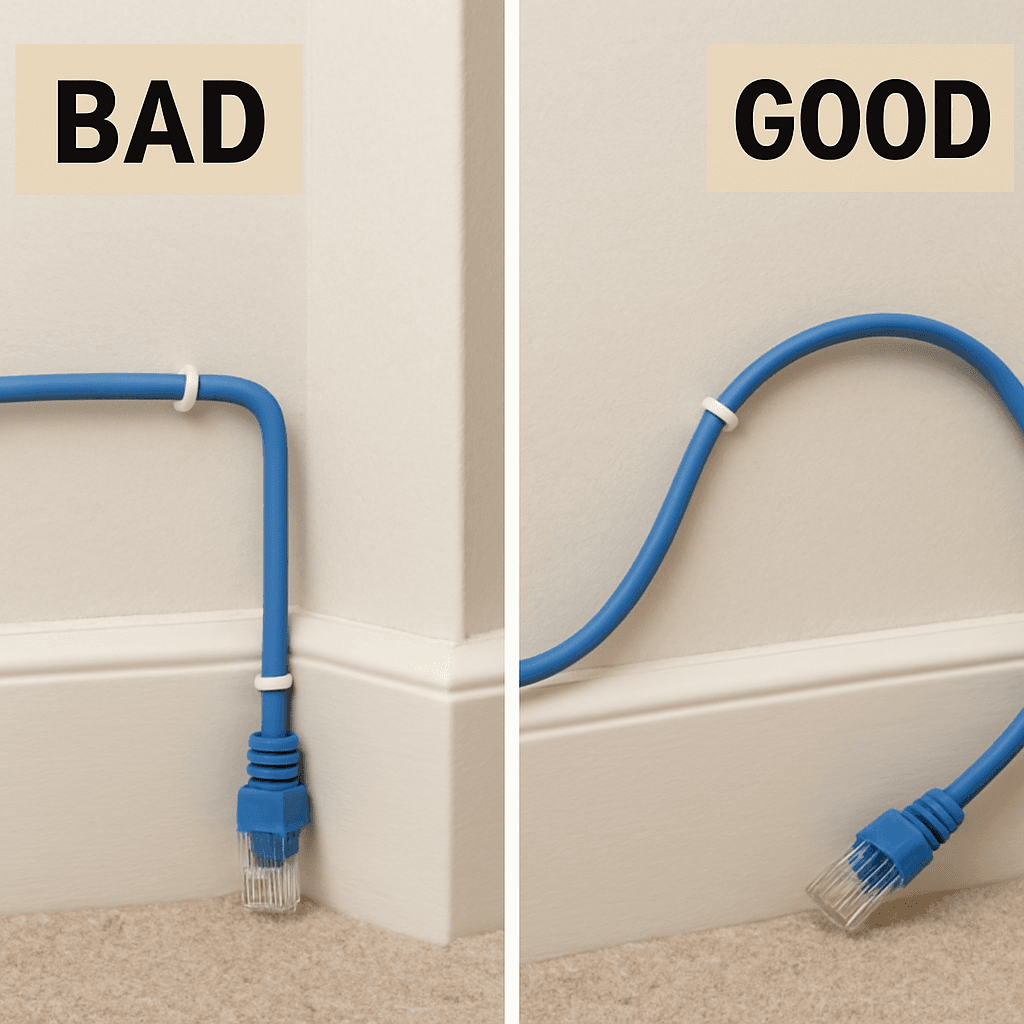
Mistake #4: When Your Cable's Journey is Just Too Long
Bigger homes and offices often require long cable runs, but does cable length affect internet speed? The answer is a resounding yes. Think of a data signal traveling down an Ethernet cable like a person's voice traveling across a field. The closer you are, the clearer you hear them. As they get farther away, their voice fades until it becomes an indecipherable whisper. Your data signal experiences the exact same problem; it gets progressively weaker the farther it has to travel. This fading effect is known as signal attenuation. For standard copper Ethernet cables, this becomes a major issue after a certain point. The maximum recommended length for a single cable run to deliver its full, advertised speed is 100 meters (or 328 feet). Beyond this, speed degradation is not a possibility—it's a certainty. You might still get a connection on a 400-foot cable, but you won't be getting the gigabit speeds you expect. Instead, you'll see frequent drops and speeds that are a fraction of what they should be. So while that super-long cable you found online might seem like the perfect solution for connecting the router in the basement to the office upstairs, it could be the hidden source of your network headaches. The connection works just enough to fool you, but it fails under pressure during a big download or important video call. However, even a perfectly short, gently curved cable can fail if the final inches of the journey are a mess. This brings us to the most common—and most overlooked—mistake of all.
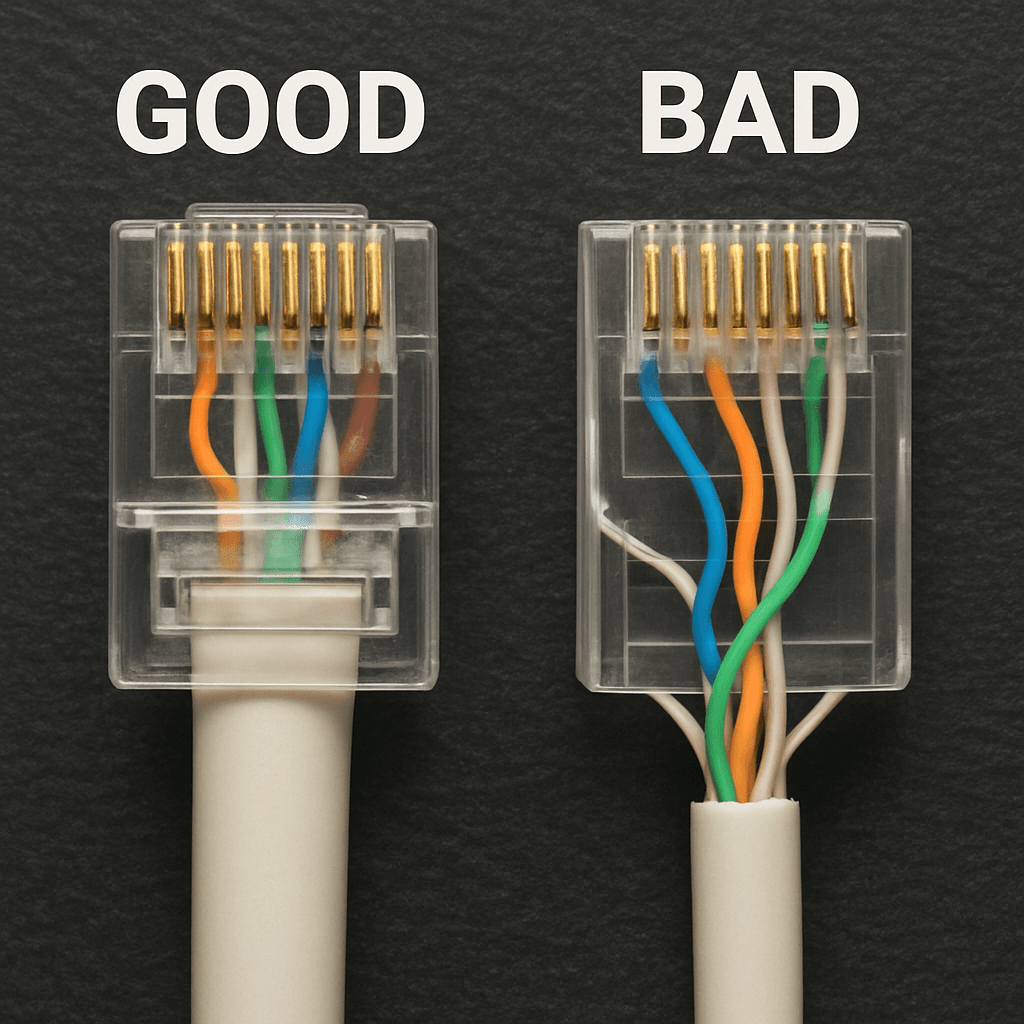
Mistake #5: The 'Last Inch' Fumble That Cripples a Perfect Cable Run
You can have the best cable, cut to the perfect length, and run far from any power lines, but all that work can be undone in the last inch. This final connection point—the plastic RJ45 connector at the end of the cable—is where most DIY and even some professional installations fail. Attaching this connector properly is a skill called cable termination, and getting it wrong is like attaching a leaky, sputtering nozzle to a high-pressure firehose. You lose all the performance right at the finish line. Inside every Ethernet cable, tiny wires are tightly twisted in pairs. As you learned earlier, these twists are your cable’s secret weapon against crosstalk and interference. The effects of improper cable termination become obvious when an installer untwists these pairs too much to fit them into the connector. That last half-inch of untwisted, parallel wire acts like a giant antenna, inviting the very signal noise the rest of the cable was designed to block. Your network is forced to constantly re-send data packets, creating slowdowns that seem to come from nowhere. So how can you spot this? Look closely at the clear plastic end of your Ethernet cable. On a bad termination, you will see a visible gap of untwisted, almost parallel colored wires between the end of the blue or grey outer jacket and the gold pins. A perfect termination, however, keeps the cable’s outer jacket pulled up tight inside the connector, ensuring the wires remain twisted right up to the very end. This vulnerability at the connection point isn't just at the ends you plug into your computer or router. It applies everywhere, from the jack in your wall to the central hub where all the cables meet. A bad patch panel can absolutely slow a network if its connections are terminated just as poorly. This is one of the key benefits of certified network cabling: an expert installer tests every single connection to guarantee it’s terminated perfectly, eliminating these hidden speed traps from your network.
Your 5-Minute Network Audit: A Checklist to Reclaim Your Lost Speed
Now you can look beyond your internet provider when faced with a buffering screen. Where you once saw a simple cord, you now see a data highway with its own rules of the road. You’ve moved beyond resetting the router and can now play network detective, spotting the hidden physical issues that choke your connection speed. This knowledge empowers you to take control of your network’s performance in a way you couldn't before. Your first mission is to use this simple network infrastructure audit checklist on your most important wired connection. Grab a coffee and take five minutes to investigate:
- Check the Print: Is it Cat5e or, ideally, Cat6? Old Cat5 cables can’t deliver modern speeds.
- Check the Neighbors: Is it bundled tightly with power cords? Separate them by a few inches to avoid interference.
- Check the Bends: Are all curves gentle, wider than a coffee mug? Sharp kinks kill performance.
- Check the Length: Is the cable excessively long? Runs approaching 300 feet can have signal problems.
- Check the Ends: Look at the plastic clip. Are the tiny wires inside neatly organized and pushed to the tip?
By running through these steps, you might discover the exact issue. It could be as simple as the gamer who found their PC was connected with a kinked Cat5 cable. A $10 Cat6 replacement later, their speed test jumped from 94 Mbps to over 750 Mbps. If you complete your audit and the slowdowns persist, you can now call your ISP or a professional installer with confidence, knowing you’ve already eliminated the most common culprits yourself. You're no longer guessing; you're troubleshooting slow ethernet like a pro.
Connect With Us
Our Office Locations
Abu Dhabi
Head Office
Dubai
Branch Office
India
Branch Office - Calicut
